Ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed vary depending on the individual’s medical history. Successful therapy and higher the overall survival rate rely on early discovery around identification. We explore the several approaches and technologies utilized in the diagnosis of cervical cancer in this thorough review. Highlighting the significance of screening initiatives and technological developments throughout this area. Is cervical cancer diagnosed through various ways how healthcare providers perform screenings?
Precancerous alterations in the cervix’s cells are frequently the initial signs of cervical cancer, which usually progresses slowly over time. Persistent infection with high-risk strains of the sexually transmitted virus human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of these alterations. Cervical cancer does not always result from HPV infections, despite their prevalence. Healthcare providers diagnose cervical cancer through methods such as Pap smears and HPV testing.
The early identification of cervical cancer and its precursor lesions is largely dependent on screening. Dr. George Papanicolaou’s invention of the Pap smear in the 1940s transformed the screening process for cervical cancer. By making it possible to identify aberrant cervical cells before they develop into cancer.
Healthcare professionals make it possible to identify aberrant cervical cells before they develop into cancer, thereby addressing cervical cancer. Based on clinical symptoms, healthcare professionals actively employ different ways to diagnose cervical cancer.
A medical professional takes cervix tissue even looks at them under a microscope. To look find all signals of abnormalities throughout a Pap screening. The Pap smear is useful, but which has drawbacks as well. Such as false-negative findings with the requirement over additional tests.
Molecular HPV testing has become a useful complement to Pap smear screening in recent years. HPV testing can identify women who are more likely to develop cervical cancer. Which looks for high-risk HPV DNA in cervical cells. Pathologists use specific methods to diagnose cervical cancer through histopathological examination. Furthermore, technological developments have helped make it possible for cytology performed. With liquids to emerge as a substitute for traditional Pap tests. Healthcare providers gather cervical cells in fluid media and treat them to produce a uniform specimen for cytological analysis in liquid-based cytology. Compared to conventional Pap smears, this approach has a number of benefits. Like as better quality of the samples and the capacity to do reflex HPV testing on the same specimen.
Advancements in Cervical Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Strategy:
Is cervical cancer diagnosed through standard ways how biopsy results are analyzed? Cervical cancer diagnosis frequently entails additional assessment of aberrant Pap. It enables enhanced vision of the uterus. When a colposcopy, a medical professional looks for abnormalities in the female reproductive system using a colposcope. The ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed involve thorough examination of tissue samples.

If healthcare providers detect cervical cancer, they may conduct further scans to assess the extent of the disease dissemination. Do healthcare providers diagnose cervical cancer with precision by using advanced methods to identify genetic alterations through molecular diagnostic techniques?
Imaging methodologies, including computed tomography, or CT, scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Healthcare providers use imaging techniques to evaluate the size and position of malignancies, as well as to determine whether surrounding tissues or other tumors are affected.
Do healthcare providers promptly diagnose cervical cancer by efficiently implementing screening programs? They utilize a combination of screening tests, clinical assessment, and pathological testing to diagnose cervical cancer. How do healthcare providers determine the most appropriate treatment approach using ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed?
Screening for Cervical Cancer:
In order to recognize precancerous or cancerous changes in the cervix before symptoms appear, testing for cervical cancer is crucial for the prompt detection and avoidance of the illness.
Healthcare professionals often perform the Pap smear, also known as the Pap test or cervical cytology, which is at the forefront of cervical cancer screening programs.
Improved patient outcomes contribute by various ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed.
During this testing process, healthcare professionals take tissue samples from the cervix, usually during an examination of the pelvis, and subsequently view them under a magnifying glass to check for anomalies.
Utilizing a microscope to see the cervix, a medical professional collects cells from its surface using a very small tool the scraper during a Pap smear. After that, healthcare professionals put these cells in a liquid medium or on a glass slide and submit them to a lab for examination. Do healthcare professionals accurately diagnose cervical cancer by combining different ways how they utilize diagnostic tests?
As part of cervical cancer assessment, medical professionals may advise HPV testing while alongside standard Pap smears. The ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed ensure comprehensive evaluation of the disease. The process of HPV testing include looking for high-risk HPV types, especially types 16 and 18, which have a significant association with the onset of cervical cancer.

As advised by medical standards, routine screening with Pap smears and HPV testing can assist in identifying cervical anomalies promptly, when therapy is most successful.
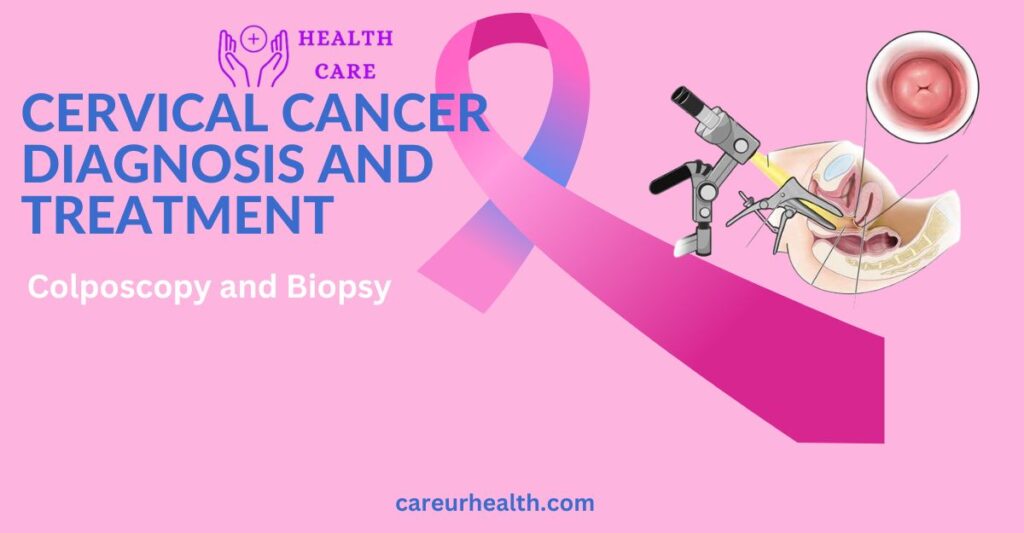
Colposcopy and Biopsy:
If anomalies are found after an HPV test, healthcare providers may deem it necessary to perform a colposcopy for further evaluation. They utilize a crucial diagnostic technique called colposcopy to carefully inspect the cervix for any worrisome spots that could indicate malignant or precancerous alterations. During this procedure, healthcare providers use a colposcope, a specialized magnifying device that offers a comprehensive view of the cervix.
Similar to a pelvic exam, the patient rests on a testing surface during a colonoscopy, and the medical professional uses a scope to enter into the vagina to view the cervix. Her cervical area can then be closely examined by the clinician by positioning the colposcope related to the vaginal entrance. The medical professional can spot potential odd spots thanks to this colposcope’s illumination and magnifying features.
Do innovative ways enhance detection methods for diagnosing cervical cancer through technology?
If worrisome abnormalities are found following a colposcopy, healthcare professionals may need to perform a biopsy. Removing a tiny sample of tissue from the afflicted region for additional testing. For diagnosing cervical cancer effectively through ways that are effective, interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals relies upon. Several biopsy techniques apply depending on the size and location of the lesion, but generally speaking, they entail healthcare professionals taking a small sample of tissue with specific instruments.
Imaging Studies:
These investigations offer comprehensive physiological information regarding the cervix, surrounding tissues, and any possible cancerous dissemination to other locations.
Healthcare providers frequently employ CAT (CT) imaging to evaluate cervical cancer, utilizing a variety of imaging methods, each with specific benefits and insights into the condition.
A CT scan involves taking many X-ray pictures of the human body throughout multiple vantage points. The gadget then merges these pictures to produce intricate longitudinal pictures.

One useful tomography technique for evaluating cervical cancer is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI produces finely comprehensive images regarding the physique’s soft tissues by using electromagnetic radiation and high magnetic fields. Superb contrasting quality offered by MRI makes it possible to clearly see cervical cancers along with how they relate to nearby tissues. When evaluating tumor size, cervical stroma invasion, and involvement of the pelvic margins with parametrium, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is especially helpful. Furthermore, MRI has a high degree of sensitivity in identifying lymphatic metastases, which helps with precise illness stages.
Occasionally, healthcare providers combine PET (positron emission tomography) images with scans using CT or MRI to obtain useful data on malignant tissues. The ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed provide valuable information for treatment planning.
Cervical Biopsy and Histopathology:
Is cervical cancer diagnosed reliably through standardized ways how diagnostic protocols are followed? One essential step towards the diagnosis of cervical cancer is the cervical biopsy. Healthcare providers employ a variety of methods, including punch biopsies, cone biopsies, and looping electrosurgical eradication process (LEEP), to take tissues from the cervix. Timely diagnosis of cervical cancer facilitates timely initiation of treatment. Using these methods, medical professionals can take tissue specimens from various cervix regions based on probable abnormalities found throughout a colposcopy or clinical examination.
When suspecting or confirming cervical cancer, healthcare providers actively utilize diagnostic imaging tests to assess the extent of the disease and establish its stage. Do healthcare providers accurately diagnose cervical cancer by following evidence-based ways how they implement diagnostic guidelines? These tests provide comprehensive anatomical details on the cervix, surrounding tissues, and possible metastases of cancer. Healthcare providers assess cervical cancer using a variety of imaging options, each of which offers specific benefits for disease-related discoveries.
Additional Diagnostic Tests:
Healthcare providers may require diagnostics outside screenings, including biopsies, to provide a complete evaluation regarding the disease’s features, including its extent, in the entire diagnostic arsenal against cervical cancer.
These additional diagnostic tests help to clarify a diagnosis, guide therapy choices, and provide a precise prediction. The ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed ensure optimal management of the disease.
Cervical cancer diagnosis is becoming more and more dependent on genetic therapeutic instruments within alongside morphological around histologic examinations. Healthcare providers use molecular tests such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to identify certain genetic changes linked to cervical cancer. By amplifying and analyzing the sequences of DNA, PCR makes it possible to find HPV DNA . On the other hand, FISH uses particular DNA sequences to visualize cells and provides data concerning genetic amplifiers. Other anomalies in the chromosomes that may indicate malignant alterations.
Conclusion:
In summary, we have a comprehensive strategy is used to diagnose cervical cancer. Including assessment, medical evaluation, biopsies, histological analysis, as well as, in certain situations, further tests for diagnosis. Early identification of cervical anomalies through checks, such as cervical smears and HPV testing. It is crucial for prompt intervention and the prevention of cancer development. Physical assessment, which includes a colposcopy alongside vaginal exam. Gives significant details regarding the existence of suspicious lesions or symptoms that might indicate the disease.
Is cervical cancer diagnosed effectively through standardized ways how quality assurance measures are implemented in diagnostic laboratories? Certain characteristics of cervical cancer may require extra investigation in certain circumstances. The cervical canal is the objective of endocervical curettage (ECC), and sentinel lymph node biopsy.
In general, enhancing prognosis for individuals with cervical cancer requires prompt detection and correct diagnosis. Molecular assays and imaging modalities are two examples of how developments in diagnostics. Is cervical cancer diagnosed early through proactive ways how individuals seek medical attention for symptoms or concerns? Are helping to improve patient care by helping doctors customize treatment strategies depending on unique client features. In all, here are the various ways how cervical cancer is diagnosed and underscore the importance of regular health screenings for women of all ages.
FAQ
1. Which were the main techniques to diagnose cervical cancer?
The main ways of identifying cervical cancer include imaging investigations, biopsies, colposcopy, HPV testing, and Pap smear monitoring.
2. When must women get screened for cervical cancer?
According to instructions, women between the ages of 21 and 29 should get a Pap smear each three decades in order to test for cervical cancer, which should begin at the age of 21.
3. How can a Pap smear result that is abnormal mean?
An atypical Pap smear result reveals the presence of aberrant cervical cells, which various factors such as HPV infection or precancerous alterations can cause. Healthcare providers often recommend conducting additional investigations, such as a tissue biopsy or colposcopy, to further examine the abnormalities. To ascertain the relevance of the aberrant results.
4. How might a colonoscopy help identify cervical cancer?
Employing a colposcope, medical personnel can directly examine the cervix during a colposcopy to check for any discrepancies. When anomalies detect through HPV testing or a cervical examination, healthcare providers often proceed with further investigation. If they identify any questionable malignancies, they may conduct a biopsy to obtain tissue samples for additional examination.
5. What role do imaging procedures play throughout the cervical cancer diagnostic process?
By imaging methods including CT, MRI, and PET scans. These are techniques for imaging support medical professionals in planning therapies and therapy response. Monitoring by making the cervix, surrounding lymph nodes, and other pelvic tissues visible.
JJ Medicine