Introduction
Chickenpox vs Measles comprise two infectious viral diseases that often strike youngsters but can strike adults as well. Although the symptoms and modes for transmitting of both of these illnesses are somewhat similar, there are important distinctions as well, such as the agents responsible, the accessibility of vaccinations, and possible side effects.
Chickenpox vs measles – agents of Causation:
Chickenpox: A part of the herpesvirus family, varicella-zoster virus (VZV) generates chickenpox.
Measles: This viral virus, which belongs to the Paramyxoviridae family, is the root of the disease.
Chickenpox vs measles – Transmission
Chickenpox: Transmission can be transmitted by the infected person. It can be transmitted in air or by the droplets of the virus. An infected person has rashes on his body, if you touch then you might also get this virus.
Measles: sneeze from the infected person or cough lets out then virus present in air in the form of airborne droplets. This helps the spreading of this disease. Close contact with that person also gets this virus.
Signs of measles vs chicken pox
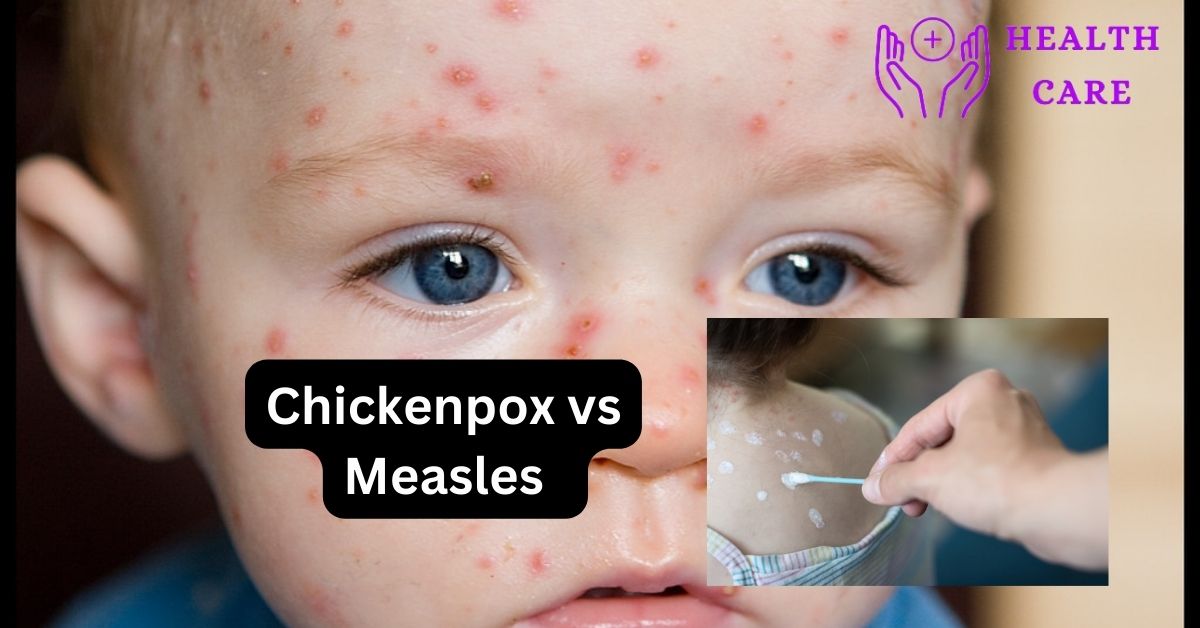
Chickenpox: it involves rashes, itchiness, sometimes fever and headaches. There are blisters also in Chickenpox. Little red dots that soon turn into itchy blisters eventually crusting over are the initial signs of the rashes.
Measles: it includes red or irritated eyes (conjunctivitis). A person also gets a high fever or temperature, a runny nose. It also consists the rashes that usually begin on one’s face and move down to the rest of the body.
Problems of chickenpox vs measles
Chickenpox: Although typically not severe, complications can arise from chickenpox, particularly in adults, expectant mothers, infants, and people with compromised immune responses. Bacterial skin sickness, pneumonia, encephalitis, as well as, in rare cases, even death are possible consequences.
Measles: Measles can lead to serious consequences, especially in adults and also young kids. These might involve pneumonia, encephalitis (brain inflammation), and under extreme circumstances, even death. Premature delivery, poor birth weight, and miscarriage can result from the measles virus during pregnancy.
Therapy of chickenpox vs measles
Treatment for chickenpox usually consists of controlling symptoms like fever plus itching. In some situations, antiviral drugs may be recommended, especially for people who are more susceptible to problems.
Measles: There isn’t a particular antiviral therapy for the disease. The cornerstone of medical care is assistance, which aims to reduce symptoms and avoid consequences.
Conclusion
There are significant distinctions between measles and chickenpox about of potential sequelae, vaccination accessibility, signs, and causative agents, even though both viral illnesses mostly afflict children. The requirement for such illnesses has been significantly reduced by vaccination, highlighting the critical role immunisation plays in public health initiatives to manage infectious diseases and stop outbreaks. Even though vaccinations are readily available, continuous efforts are required to guarantee high immunisation rates and stop the comeback of these potentially dangerous illnesses.